Useful tips on how to store, use, send and spend Bitcoin privately.
Bitcoin is pseudonymous. This simply means that it reveals some information about the owners of the wallets and addresses, while it keeps other information hidden. That however does not mean that the people who want to keep their privacy and anonymity are not off the hook.
On the contrary, since Bitcoin is not anonymous, the users of Bitcoin that want to keep their privacy, need to take active steps in order to do so. What steps can they make and why would they do so? That is something that we will explore today.
Pseudonymity as a key feature
While we have explored some of the features and characteristics of Bitcoin, properly understanding pseudonymity is key to understanding how the users can stay anonymous in this world. This is because Bitcoin still reveals some information about the users of this global monetary network.
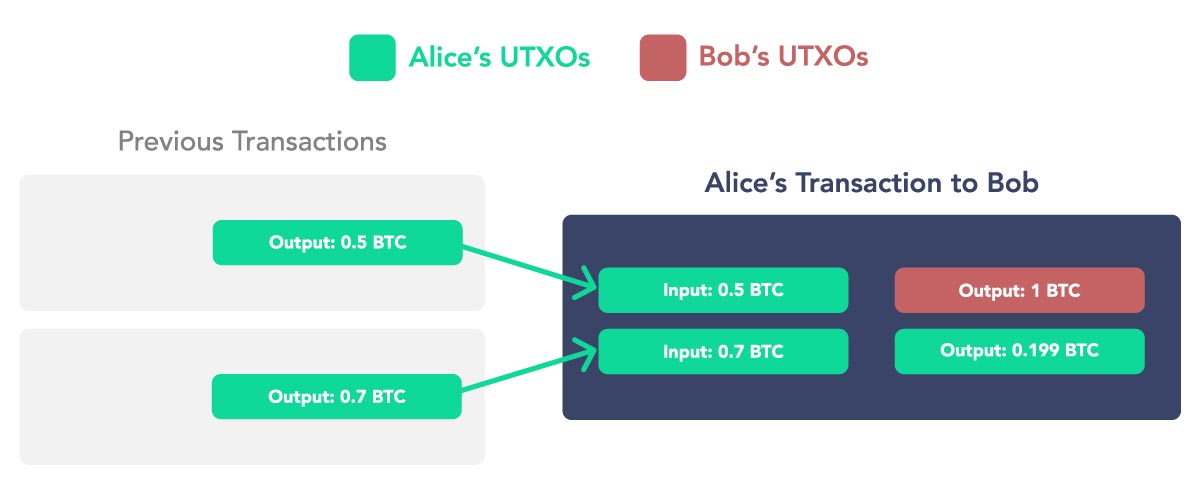
For simplicity, let’s take the example of Alice and Bob. Alice has two UTXOs (unspent transaction output) worth 1.2 BTC, divided into two inputs of 0.5 BTC and 0.7 BTC. Alice wants to send 1 BTC to Bob. To do so, she creates a transaction, which creates two new outputs, the first one worth 1 BTC (Bob) and the second one worth 0.199 BTC (Alice). In this case, the 0.001 BTC is paid to miners as a transaction fee.
And while this creates two new addresses, if the observer of the blockchain, such as a chain analysis company that we will talk about more later, knew that Alice had 1.2 BTC before, they know that one of those outputs is probably hers. This can be deduced through applying heuristics and some logic on top of how Bitcoin works.
However, if this should work, the chain analysis companies need to have at least some kind of information about the owners of the UTXOs or the addresses. This can be done through different KYC/AML compliance practices with different exchanges, custodians or providers of crypto services. Thus, once they know some KYC information about the specific UTXO, once it is spent, the chain analysis company can try to determine whether it was sent to a different owner or the same.
What is KYC/AML?
That is a simple explanation of what can happen once the owner of any wallet or UTXO reveals their identity (whether willingly or unwillingly) or if their identity is connected somehow to the address by these companies. However, how does that happen?
There are several possibilities of how an address or UTXO can be connected to someone’s identity. Probably the easiest way it can happen is through KYC (know-your-customer) practices. These depend mostly on jurisdictions, in which different crypto service providers operate. But most of them have already implemented or are trying to implement some form of KYC.
If that happens, the providers of cryptocurrency services are bound by law to collect different KYC information about their customers. These can be anything from name, email address and home address, to more extensive KYC such as bank statements, ID or passport. In fact, most KYC exchanges or custodians will ask for at least some proof of identification, thus connecting the wallets immediately with your identity.
What is chain analysis?
Even if that does not happen, there is a chain analysis that can help governments or regulators with identifying who owns what. These types of companies, such as Chainalysis, were created with many purposes. The main one however is studying the blockchain, more especially the on-chain activity of the users of the given blockchain, in our case the blockchain of Bitcoin.
Through various techniques and tools, these companies can track and trace different wallets and addresses, connect them with different identities and evaluate how much capital they have. These companies often do this in cooperation with governments, who want to keep a tab on the financial aspects of its citizens.
Thus, once the user shares their identity with any custodian, brokerage or exchange, the privacy of the coins held through the given provider, as well as privacy of any wallets used before or after, is compromised. In essence, since the whole history of blockchain is transparent, if you only use one wallet or reuse addresses, once your identity is revealed, it is very likely that all of your bitcoins will be revealed with it in the eyes of the governments and chain analysis companies.
How can you protect your privacy?
To combat that, the Bitcoin users have several different techniques, tools and features that they can use to prevent the revelation of their identity. While we have already talked about CoinJoins or different anonymous bitcoin wallets, which can without any doubt help with keeping your identity private, one of the best practices the users can use is constant caution. This might sound a bit too general, which is why we will explain it a bit more.
Would you like to use, send or spend Bitcoin while protecting your financial privacy? Use Whir. A tool for an average Joe who wants to protect their privacy. Send Bitcoin privately, without KYC, using a CoinJoin transaction.
First and foremost, usage of non-KYC providers, services, platforms or products is a key. Once your identity is out there, it complicates everything. You would need to make sure to create new wallets that are anonymous, and always separate between the anonymous and non-anonymous wallets. If you combine them, all the information from both wallets automatically becomes transparent to the chain analysis companies.
Few tips and tricks
There are some ways that the Bitcoin users can have in mind to make it much more difficult for chain analysis companies or governments to track the activities of anyone in the network. We will briefly describe only a few, but there are numerous others that can provide similar privacy.
Non-KYC purchases
Probably the best way to increase your Bitcoin stash without thinking too much about different tools and techniques is simply to get your bitcoins without any KYC measures. While this can get tricky, there are different ways to do that. For instance, in some jurisdictions, it is still possible to buy bitcoins anonymously in Bitcoin ATMs. These can be sometimes limited to some extent (e.g. up to 1 000€ without KYC), but are still a pretty reasonable solution.
Another possibility of getting to non-KYC bitcoins is through different platforms that do not require the KYC as such. These can, however, change often, which means that unless you use services of providers such as Bisq, which is a non-KYC, anonymous bitcoin exchange, you might need to be very conscious of which exchange or brokerage you use.
Last but not least, the peer-to-peer market is pretty strong for Bitcoin. There are countless different groups and chat rooms where people trade their bitcoins for fiat without any need of proof ID. Sometimes these trades can work without any names, which makes everything even more anonymous. Yet it is necessary to state that you should only use groups or chat rooms that you know, because in most cases, the whole trade is based on trust.
Do not reuse addresses
Another very good and relatively easy practice to help you improve your privacy is to never use any address twice. With bitcoin it is extremely easy to generate new addresses. This makes it much harder for the analytic companies not only to trace, but also to connect and combine different wallets or addresses with a name or identity.
Lightning Network
What can help with the privacy is also usage of off-chain solutions. The logic there is pretty straightforward. If you do not want to have a transaction recorded in the blockchain (on-chain), use an off-chain solution. Probably the best example of a layer-2 off-chain solution is Lightning Network that is seeing a huge uptrend in the past months in terms of its capacity, usage, number of users or transactions.
Basically, any metric connected to Lightning Network is seeing a rise. This is definitely not only thanks to almost instant and cheap transactions, but also due to the fact that it provides complete anonymity. The transactions through Lightning Network are off-chain and unless your wallet does not require KYC, which it should not, no identity should be connected to any transaction.
Conclusion
The privacy while sending Bitcoin is not an inherent characteristic, but an important feature that can be improved upon. There are several tools, techniques or practices that anyone can keep in mind to enhance their chances of being anonymous or private in the world that is transparent.
Would you like to use, send or spend Bitcoin while protecting your financial privacy? Use Whir. A tool for an average Joe who wants to protect their privacy. Send Bitcoin privately, without KYC, using a CoinJoin transaction.
––
If you liked this article, please share it on Twitter.
Disclaimer: This article does not serve as a piece of financial advice or encouragement and inducement for the usage of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies. Its primary role is informative, explanatory, and educational. The readers have to decide themselves whether to use or not to use these types of services.